| Previous Page | Up One Level |
Lecture Slides available: PDF PowerPoint
Advanced ER Mapping
Contents
- Mapping parallel relationships
- Mapping 1:m in unary relationships
- Mapping superclasses and subclasses
- Example
Overview
- map parallel relationships into relations
- map unary relationships into relations
- map superclasses and subclasses into relations
Mapping parallel relationships
Parallel relationships occur when there are two or more relationships between two entity types (e.g. employees own and service cars).
-
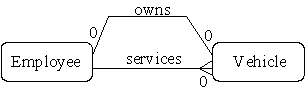
- Figure : Parallel Relationships
- In order to distinguish between the two roles we can give the foreign keys different names.
- Each relationship is mapped according to the rules, and we end up with two foreign keys added to the Vehicle table.
- So we add the employee_no as the owner_no in order to represent the `owns' relationship.
- We then add the employee_no as the serviced_by attribute in order to represent the `services' relationship.
- Before mapping
Employee(employee_no,...) Vehicle(registration_no,...)
- After mapping
Employee(employee_no,...)
Vehicle(registration_no,owner_no,serviced_by,...)
Mapping 1:m in unary relationships
-
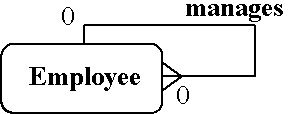
- Figure : Mapping recursive relationships
- Employees manage employees
- Each employee has an employee_no with is the primary key
- We represent the manages relationship by adding a manager_no as a foreign key.
- This is in fact the employee_no of the manager.
- It is given a different name to clearly convey what it represents, and to ensure that all the entity type's attributes have unique names, as to do otherwise would be invalid.
- After mapping
Employee(employee_no,manager_no, name,...)
- So in general, for unary 1:n relationships, the foreign key is the primary key of the same table, but is given a different name.
- Note that the relationship is optional in both directions because not all staff can be managers, and the top manager is not managed by anybody else.
Mapping superclasses and subclasses
There are three ways of implementing superclasses and subclasses and it depends on the application which will be the most suitable.
Only the first method is a true reflection of the superclasses and subclasses and if either of the other methods is preferential then the model should not have subclasses.
- One relation for the superclass and one relation for each subclass.
- One relation for each subclass.
- One relation for the superclass.
Example
-
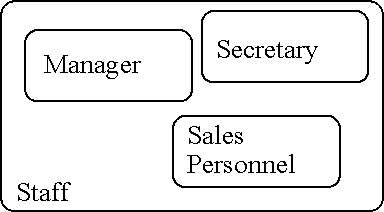
- Figure : Superclass/Subclass mapping example
Staff(staff_no,name,address,dob) Manager(bonus) Secretary(wp_skills) Sales_personnel(sales_area, car_allowance)
One relation for the superclass and one relation for each subclass:
Staff(staff_no,name,address,dob) Manager(staff_no,bonus) Secretary(staff_no,wp_skills) Sales_personnel(staff_no,sales_area, car_allowance)
The primary key of the superclass is mapped into each subclass and becomes the subclasses primary key. This represents most closely the EER model. However it can cause efficiency problems as there needs to be a lot of joins if the additional information is often needed for all staff.
One relation for each subclass:
Manager(staff_no,name,address,dob,bonus) Secretary(staff_no,name,address,dob,wp_skills) Sales_personnel(staff_no,name,address,dob,sales_area, car_allowance)
All attributes are mapped into each subclass. It is equivalent to having three separate entity types and no superclass.
It is useful if there are no overlapping entities and there are no relationships between the superclass and other entity types. It is poor if the subclasses are not disjoint as there is data duplication in each relation which can cause problems with consistency.
One relation for the superclass:
Staff(staff_no,name,address,dob, bonus, wp_skills, sales_area, car_allowance)
This represents a single entity type with no subclasses.
This is no good if the subclasses are not disjoint or if there are relationships between the subclasses and the other entities.
In addition, there will be many null fields if the subclasses do not overlap a lot. However, it avoids any joins to get additional information about each member of staff.
| Previous Page | Up One Level |
| ||||
| ||||
|